
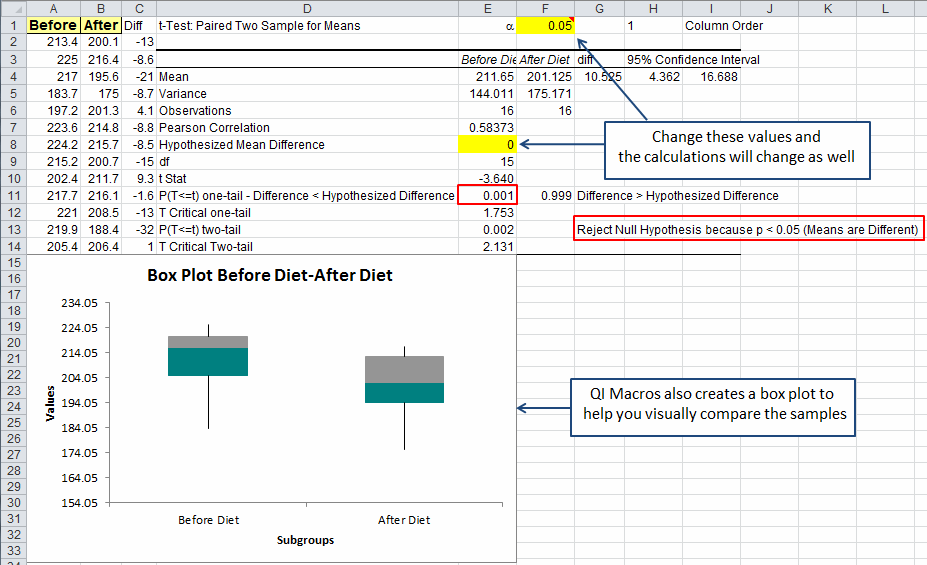
The p-value is a number, calculated from a statistical test, that describes how likely you are to have found a particular set of observations if the null hypothesis were true. QI Macros results are also interactive and let you change the significance level and Hypothesized Difference in Means to see what impact those changes have on your results. The p-value explained Published on Jby Rebecca Bevans. It further interprets whether the means are equal (the same/are not different) or not equal (not the same/are different.) P-value formula, Z-score formula, T-statistic. QI Macros compares the p-value to the significance level for you and translates that into whether you can reject or cannot reject the null hypothesis. Powerful p-value calculator online: calculate statistical significance using a Z-test or T-test statistic. Example of a QI Macros t test and p value calculation 01 are the most common levels of significance used. Weak evidence against the null hypothesisĮvidence does not point strongly either way Strong evidence against the null hypothesis
#P value from hypothesis test calculator free#
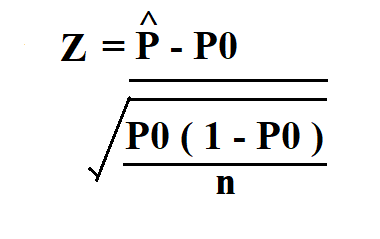
Notice that this is a one sample t test calculator. To use the calculator, simply input the z-score for the standard normal distribution, select the p-value type, and.
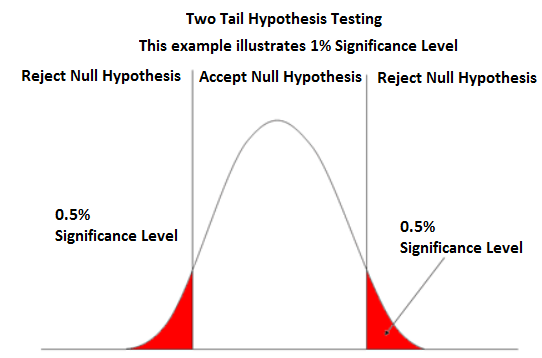
It also generates a normal curve and shades in the area that represents the p-value. What happens with the t-test when I have 2 samples You can use this p-value calculator to calculate the right-tailed, left-tailed, or two-tailed p-values for a given z-score. The null hypothesis is rejected when the t-statistic lies on the rejection region, which is determined by the significance level (\(\alpha\)) the type of tail (two-tailed, left-tailed or right-tailed) and the The color of that cell will determine which p-value and confidence interval you will use: 1) To obtain the critical values (cut-off values) for your test, 2) To obtain the test statistic, p-value, and confidence interval, 3) Choose the output which corresponds to your alternative hypothesis.
#P value from hypothesis test calculator how to#
How to Compute the t-statistic for one sample? Type I error occurs when we reject a true null hypothesis, and the Type II error occurs when we fail to reject a false null hypothesis Left-tailed / Right-tailed / Two-tailed) Step 3 - Click on 'Calculate' button to get the p-value. Step 3 - Select the alternative hypothesis (i.e. In a hypothesis tests there are two types of errors. Step 1 - Enter the value of t -test statistic. The p-value is the probability of obtaining sample results as extreme or more extreme than the sample results obtained, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true The standard significance level is 0.05 by default. Since this number is greater than our alpha level of 0.05, we fail to reject the null hypothesis of our test. Our calculator determines the p-value from test statistic, and provides the decision to be made about the null hypothesis. The p-value for a test statistic t of 1.34 for a two-tailed test with 22 degrees of freedom is 0.19392. The main principle of hypothesis testing is that the null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic obtained is sufficiently unlikely under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true In order to find this p-value, we can’t use the t distribution table because it only provides us with critical values, not p-values. The main properties of a one sample t-test for one population mean are:įor a t-test for one mean, the sampling distribution used for the t-test statistic (which is the distribution of the test statistic under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true) corresponds to the t-distribution, with n-1 degrees of freedom (instead of being the standard normal distribution, as in the case of a z-test for one mean)ĭepending on our knowledge about the "no effect" situation, the t-test can be two-tailed, left-tailed or right-tailed The null hypothesis is a statement about the population mean, under the assumption of no effect, and the alternative hypothesis is the complementary hypothesis to the null hypothesis. Note that in Excel 2007 we calculate p-value TDIST(t, df, 2) TDIST(3.66, 39.
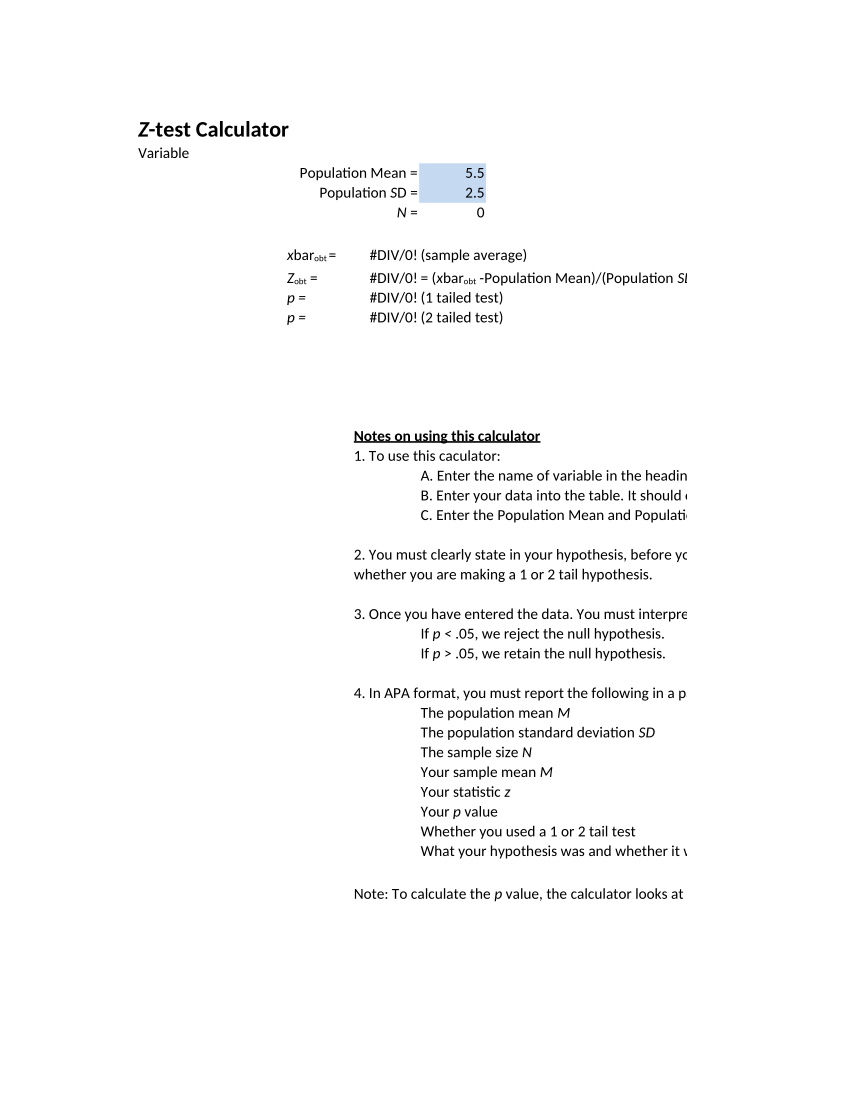
Calculate the P-value for a 2-tailed test pt(-1.4, 10) + (1 - pt(1. The test has two complementary hypotheses, the null and the alternative hypothesis. Since tobs 3.66 > 2.02 once again we reject the null hypothesis. The null and alternative statistical hypotheses for a two-tail test are. How to Conduct a T-test for One Population Mean? This t-test, unlike the z-test, does not need to know the population standard deviation \(\sigma\). So you can better interpret the results obtained by this solver: A t-test for one mean is a hypothesis test that attempts to make a claim about the population mean (\(\sigma\)). h, p ttest() also returns the p-value, p, of the test. How to use this t-test calculator for One Sample This MATLAB function returns a test decision for the null hypothesis that the data in.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
